| Contract Management Benchmarking: Manage |
 |
|
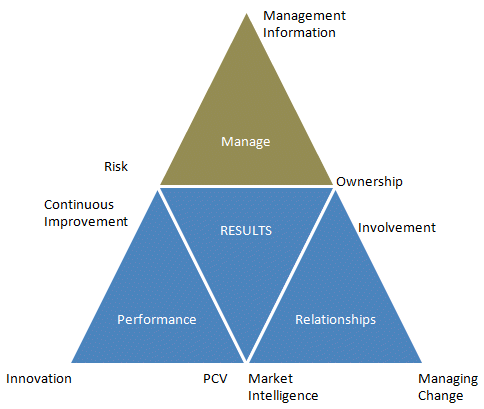
CMB: Benchmarking Model Our initial research and market review of benchmarking tools led to the development of a bespoke contract management benchmarking model. The Contract Management Benchmarking model considers the inputs and outputs (or performance) of managing contracts. The model has been developed based on research and observation of best practices across different sectors. The CMB tool considers what organisations do (inputs) to create an environment where good performance (outputs) can be achieved. The model is organised into three Categories with three Elements (nine in total) for each Category. The Categories are Manage, Performance and Relationships. Our database includes data and information from over 300 discrete submissions. 60% are listed business and represent 15 different sectors from manufacturing to distribution, aerospace, defence and marine to retail, banking and financial service to the public sector. 20% are FTSE 100 businesses.
|
||||||||||
|
CMB: Benchmarking Model
|
 |
|||||||||
|
CMB: Manage Managing contracts means different things in different sectors. This is driven by environmental factors, business context, lifecycle, market and regulatory factors as part of a complex mix of issues. Irrespective of these different factors Management Information, Risk and Ownership are key issues in formulating and executing a Contract Management strategy. Making better informed decisions based on high quality and timely information is vital. Understanding Risk and its implications is an increasing focus across the supply chain highlighted by natural disasters and changing economic forces in terms of demand and fuel costs. Ownership, perhaps the critical success factor, is key in terms of roles and responsibilities to manage and improve performance and reduce total cost. |
Manage Facts & Figures
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 |
The CMB Survey and contents are © SCMG.
CONTACT DETAILS |
