| |
CMB: Benchmarking Model
Our initial research and market review of
benchmarking tools led to the development of a bespoke Contract
Management Benchmarking model. The Contract Management Benchmarking
model considers the inputs and outputs (or performance) of managing
contracts. The model has been developed based on research and
observation of best practices across different sectors.
The CMB tool considers what organisations do
(inputs) to create an environment where good performance (outputs) can
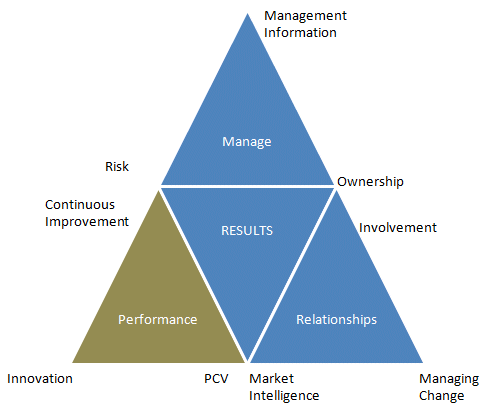
be achieved. The model is organised into three Categories with three
Elements (nine in total) for each Category. The Categories are Manage,
Performance and Relationships.
Our database includes data and information
from over 300 discrete submissions. 60% are listed business and represent 15
different sectors from manufacturing to distribution, aerospace, defence
and marine to retail, banking and financial service to the public
sector. 20% are FTSE 100 businesses.
-
75% of participants have a Contract
Management process in place,
-
28% have organised Contract Management
as a separate function,
-
Contract Management is represented at
Board level in 42% of participating businesses.
|
|
| |
CMB: Benchmarking Model
Category
|
Elements
|
Performance
How the conditions are created to enable high levels and
improving performance through continuous improvement activity,
innovation (doing things differently rather than just better) as
well as the commercial model (or bottom line) in terms of how
price issues are managed, the total cost of working together is
accurately reflected in business decision making and how mutual
opportunities to add value are recognised, measured and
considered in terms of the wider aspects of working together,
incentives and reward.
|
Continuous Improvement
The focus and level of activity and role that continuous
improvement activities and techniques are considered and applied
in relation to the contract and joint activities (or processes)
between client and supplier including forecasting and planning,
operational performance and performance improvement and cost
reduction.
|
Innovation
The level of activity and focus on doing things differently or
innovating (versus continuous improvement which is doing the
same things better) in relation to processes, how people are
organised and work together or technology
applied to deliver improved performance.
|
Price, Cost and Value
How commercial performance is managed in overall terms to
consider the role of price and margin as part of a better and
more informed total cost perspective e.g. a higher price may be
worth paying if the total cost is lower, the focus on margins
and the level of openness and transparency on prices and cost as
well as the potential and opportunities to consider the wider
issues of value add or how one party can or may create value add
opportunities by providing access to new or different markets or
can leverage improvements or technology to create more market
share or revenue for example.
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
CMB: Performance
Performance is now multi-faceted and
traditional measures of quality, delivery and price are limited in terms
of considering the wider aspects of maintaining and improving
performance. Performance must be considered in commercial terms but
total cost and environmental factors and sustainability drive different
thinking and decision making. From a commercial perspective price, cost
and value provide a bigger picture than price alone. Continuous
improvement has more potential than a static approach where the status
quo is considered acceptable. Innovation, or doing things differently,
rather than the same things better might provide a step change or
provide a more sustainable solution. |
|
Performance Facts & Figures
-
52% of participants have defined performance
improvement targets,
-
22% have dedicated performance
improvement teams,
-
22% have targets for innovation as part
of contract delivery,
-
31% have defined price reduction targets
included in contracts,
-
43% share price reductions with
suppliers,
-
34% measure their own cost of managing
contracts.
|
|



