| |
CMB: Benchmarking Model
Our initial research and market review of
benchmarking tools led to the development of a bespoke contract
management benchmarking model. The Contract Management Benchmarking
model considers the inputs and outputs (or performance) of managing
contracts. The model has been developed based on research and
observation of best practices across different sectors.
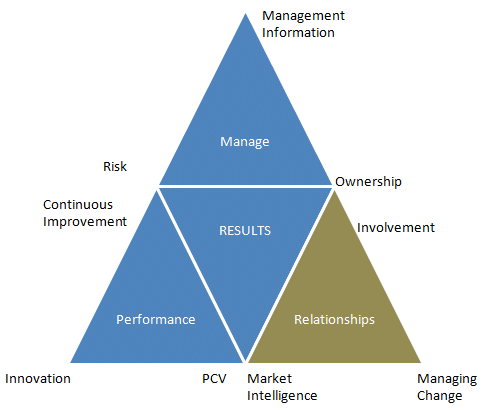
The CMB tool considers what organisations do
(inputs) to create an environment where good performance (outputs) can
be achieved. The model is organised into three categories with three
Elements (nine in total) for each Category. The Categories are Manage,
Performance and Relationships.
Our database includes data and information
from over 500 discrete submissions. 60% are listed business and represent 15
different sectors from manufacturing to distribution, aerospace, defence
and marine to retail, banking and financial service to the public
sector. 20% are FTSE 100 businesses.
-
75% of participants have a Contract
Management process in place,
-
28% have organised Contract Management
as a separate function,
-
Contract Management is represented at
Board level in 42% of participating businesses.
|
|
| |
CMB: Benchmarking Model
Category
|
Elements
|
Relationships
How the client positions themselves in relation to levels of
involvement and activity with key internal and external
stakeholders across each stage of the lifecycle process, the
relationship or positioning in the market place (as dominant or
minor player) and how that is managed as well as managing change
as the contract evolves and develops from start up to exit or
re-tendering.
|
Involvement
The level and quality of involvement with suppliers and wider
stakeholders in terms of the timing and involvement on key
issues including early involvement and better informed decision
making by considering both client and supplier issues as part of
a wider and more collaborative approach to managing and
improving performance.
|
Market Intelligence
The quality of market intelligence in terms of how it is
collected (market awareness and scanning), how it is managed and
shared internally and externally with suppliers and wider
stakeholders in terms of ensuring that current solutions are not
only fit for purpose but also up to date in terms of compliance,
technology and best practice not just to deliver static levels
of performance but to drive improvement and reduce total cost.
|
Managing Change
How change is managed across the contract management lifecycle
to consider each lifecycle stage, start up, transition and exit
stages as well as who and how stakeholders are involved and
consulted as the contract evolves and develops over its
lifecycle supported by a clear business case and decision making
process.
|
|
|
 |
|
| |
CMB: Relationships
Relationships are often quoted and seen as
the core of a contemporary contract management strategy where the style
of relationship is determined by risk and value. This is not always the
clients’ prerogative in terms of how the relationship with the market,
involvement with contractors or suppliers and managing change create a
potent mix that determines how businesses position themselves. Contract
management is about managing and optimising a relationship, or
relationships, in order to achieve the best combination of performance
and cost. |
|
Relationships Facts & Figures
-
68% collect market intelligence for key
contracts,
-
93% have a supportive environment to
discuss improvements with suppliers,
-
91% have regular operational reviews
with suppliers,
-
76% have regular strategic reviews with
suppliers,
-
49% have a formal handover from sourcing
and procurement to Contract Management,
-
56% have a formal process to identify
lessons learned from contracts.
|
|



